

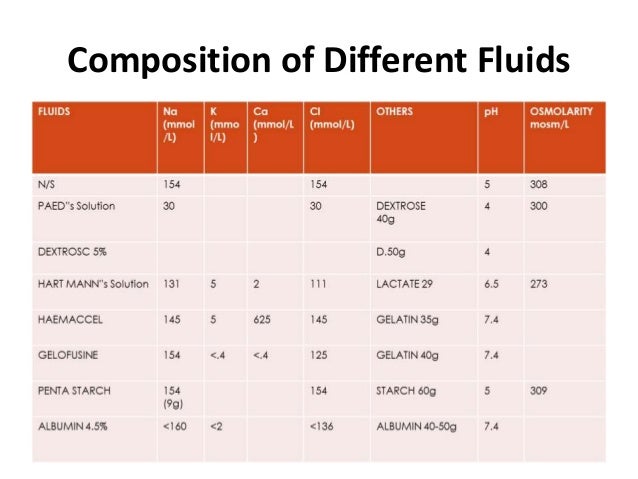
Differences between osmosis and the sodium-potassium pump Be very careful in using this half-normal saline because it may cause fluid overload or pulmonary edema. However, patients with burns, trauma, or liver disease do not need it. Using this IVF, the high level of sodium ions in the blood will be diluted and reduced. This saline solution treats too much elevation of salt in the blood or diabetic ketoacidosis.

It helps maintain the intravascular blood volume that has not collapsed significantly.Ġ.45% Normal Saline (Half Normal Saline, 0.45NaCl. The fluid contains sodium chloride, potassium chloride, calcium chloride, and sodium lactate in sterile water. It helps burns and traumatized patients. It corrects acute blood loss, electrolyte imbalance, or metabolic acidosis. This type of saline solution is mainly similar to the blood plasma concentration. Lactated Ringers (LR, Ringers Lactate, or RL) It immediately restores the intravascular blood volume and blood pressure. Thus, there is a need to give IVF with a high concentration of sodium chloride. In medical situations like these, the intravascular fluid has collapsed. It hydrates patients who experience bleeding, vomiting, diarrhea, metabolic acidosis, or shock. This type of saline solution is the most commonly used. The most common one is the 0.9% sodium chloride solution. The concentration of the sodium chloride, or saline solution, varies, and each formulation is used differently, depending on a medical condition. It is composed of sodium chloride and sterile water. On most occasions, saline, also known as saline solution, is used. When there is a problem in one fluid compartment, using intravenous fluids correct it.
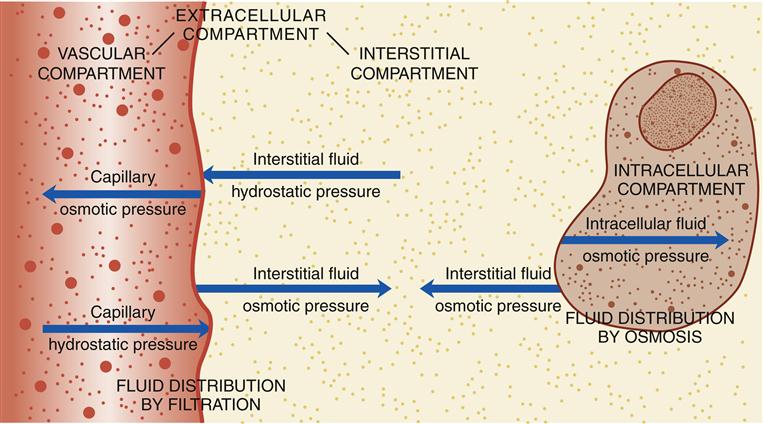
Thus, the concentrations of sodium inside the cells are maintained at low levels, preventing water from entering in large and uncontrollable amounts. They finally settle into the intercellular spaces. This mechanism pumps out the extra sodium molecules that are inside the cells. It is via the so-called sodium-potassium pump. Thus, there is another mechanism that lowers the concentration of sodium inside the cells. Preventing the entry of too much water inside the cells is critical in the maintenance of human lives. It contains salts needed to hold water in the extracellular spaces. Hence, saline is used in intravenous fluids and not pure water. Swelling of cells takes place, and the tissues will soon swell as well. If intravenous fluids use pure water, the concentration of sodium and chloride in the intravascular space will be diluted and lowered, forcing water to enter the cells and the areas in between them. The purpose of this is to ensure that water stays in the extracellular spaces and does not enter the cells. Whereas their amounts in the intracellular compartments are low. Typically, the concentrations of sodium and chloride inside the blood vessels and between cells are high.
The most common ones are sodium (Na+), chloride (Cl-), and potassium (K+). In the three fluid compartments, there are various kinds of electrolytes. Roles of electrolytes in the fluid compartments For this very reason, intravenous fluids use a saline solution containing salts as a vehicle and not pure water. Thus, some parts of the body, such as the lower legs, begin to swell. Higher salt concentration inside the cells causes the water to shift from the blood vessels and between cells into the intracellular fluid, causing the cells to swell. Infusion of pure water into the patient’s vascular system dilutes the salt concentration inside the blood vessels. Since there are more solutes or salts in compartment B than A, fluid moves from A to B.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
